How to Become an Electrician: 6 Basic Steps to Journeyman Status
Becoming a journeyman electrician might be easier than you realize. The path into this reliable trade often looks like this: First, get a basic education, including optional pre-apprenticeship training at a trade school. Then, complete a paid, multi-year apprenticeship. Finally, get licensed or certified (if required).
Here's a general overview of how to become an electrician when you're starting from scratch: First, make sure that you've earned a high school diploma (or the equivalent such as a GED). Next, take the optional (but recommended) step of completing a pre-apprenticeship electrician-training program at a local trade, technical, or vocational school. After that, apply for an electrician apprenticeship and, if required, register as an electrician apprentice or trainee in your state. Complete your four- or five-year apprenticeship under the guidance of a master or journeyperson* electrician. Finally, if required, get your electrician license or become certified in your state and/or municipality, which may involve passing an exam.
Those are the basic steps to becoming an electrician. Of course, it's wise to look into each of those steps in more detail so that you know exactly what to expect. After all, confidence is an important trait to develop, especially while learning to be an electrician. The more you know, the greater your confidence will be as you move forward. And electrician careers are worth the attention. They often provide reliable and meaningful ways to earn good wages and benefits.


How To Become An Electrician In 6 Steps
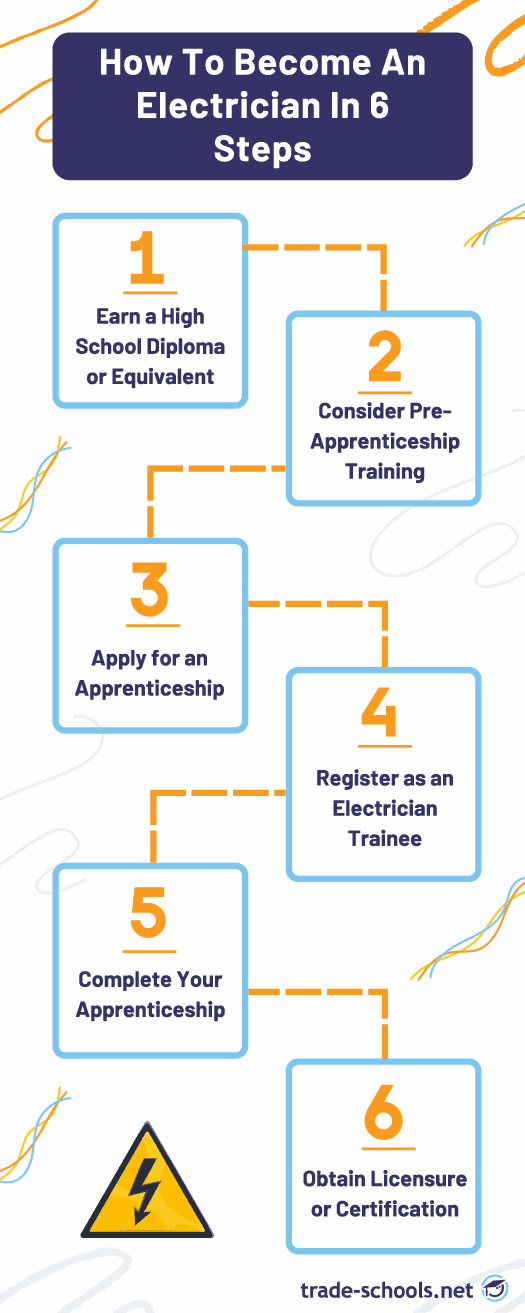
1. Earn a high school diploma or equivalent
This step is essential. You may not be able to progress any further until you can show that you've successfully completed high school or earned a GED or other type of equivalency certification. It's one of the most basic educational requirements that you'll need to meet before you can become an electrician.
If you're still in high school, choose your courses carefully. Algebra and trigonometry are important, since such math is used by electricians to measure wiring lengths, determine the angle of a circuit, and calculate the force of an electrical current. In addition, you may want to pay special attention to subjects like physics and English. Shop and mechanical drawing classes are also helpful. After all, being an electrician requires knowing how to read technical documents and understand basic scientific concepts.
If you are an adult who didn't complete high school, it's possible to earn your high school diploma online. This is a convenient way to take care of this crucial first step.
2. Consider getting pre-apprenticeship training at a trade school or vocational college
Increasingly, this step is vital for making you stand out among your competition. Learning the fundamentals of electrical work is often more manageable when you aren't yet employed as an apprentice and worried about pleasing your boss. Electrician programs at trade schools, technical institutes, and career colleges provide a more comfortable introduction to this trade. They can help you gain the foundational expertise you'll need.
You'll be able to learn about the National Electric Code, workplace safety, electrical theory, and many other things that can give you a head start on other people who may apply for the same apprenticeships. Most trade school programs even include hands-on training and regular classroom instruction. That way, you'll have a solid footing when you pursue the next step of the process.
3. Apply for an apprenticeship
You can get an apprenticeship as an electrician by researching opportunities and applying as soon as you're ready. After all, you never know how many other people might be applying for the same apprentice jobs, so it's good to get a jump on them if you can. In fact, having a sense of urgency may be one of the most essential aspects of knowing how to become an electrician apprentice.
You may be able to find a local apprenticeship through the United States Department of Labor or by exploring newspaper classifieds and online job boards. In addition, electrical apprenticeship openings periodically become available through organizations such as:
You may need to pass a basic aptitude exam as part of the application process. The exam will most likely test your reading comprehension and ability to perform simple arithmetic and first-year algebra. In addition, you will need to pass a job interview. And you may need to meet specific physical requirements, pass a drug test, and demonstrate a certain level of mechanical aptitude.
That's why many employers recommend getting some basic electrical training before applying for the apprenticeships they sponsor. Trade and vocational schools specialize in helping students get up to speed on what they'll need to know to succeed during the application process.
4. Register as an electrician trainee or apprentice in your state (if required)
Some states, such as California and Texas, require electrical apprentices to register before being allowed to work on actual job sites. It's generally a straightforward step since it only involves filling out a form and potentially paying a small fee. But every state has its requirements, so be sure to check with your state's licensing, labor, or consumer affairs department.
5. Complete your apprenticeship
This step is the heart of the whole process. Your apprenticeship will combine on-the-job training with online and classroom courses. You'll be mentored and supervised by a master or journeyperson electrician throughout four to five years of training. And you'll get paid an hourly wage.
Along the way, you'll study essential concepts and receive practical job-site experiences related to a typical electrician job description. For example, you'll get the opportunity to practice and learn about aspects of the trade such as:
- Reading construction blueprints and technical diagrams for electrical plans
- Installing, repairing, and maintaining electrical wiring, lighting fixtures, electricity distribution equipment, and various control systems
- Making sure that all work complies with the National Electric Code as well as state and local regulations
- Testing and inspecting electrical systems and components for problems by using special devices
You'll perform very basic tasks at the beginning of your apprenticeship. But you will gradually get to carry out more and more complex tasks as you refine your skills and practical understanding of relevant concepts. By the end of your apprenticeship, you will likely be capable of performing a full range of construction- and maintenance-related electrical work at the journeyperson level.
6. Get licensed or certified in your state and/or municipality (if required)
One of the most important things to understand when exploring how to become a licensed electrician is that every state sets its own standards. In most states, you need a license to be a qualified electrician. Some states (such as Illinois and Pennsylvania) don't license electricians at the state level; however, some towns and cities within those states do have licensing requirements.
So it's essential to contact your state and the municipalities you plan to work in. Ask them if you need a license to perform electrical work. In some cases, you may need a license to work as an employee of an electrical contractor. In other cases, you may not need a license unless you plan on starting your own electrical business.
In locations that do require a license, you may have to pass an exam that tests your understanding of the National Electric Code, various electrical concepts, safety practices, and local laws and building codes. You will probably also have to prove that you have completed a certain amount of relevant classroom instruction and practical training under the supervision of a licensed journeyperson or master electrician.
Learn more about how to get an electrician's license in your region below.
Abundant Opportunities for Electricians in Clean Energy
The clean energy sector offers some of the best job prospects for electricians in the coming years. A 2021 report from the American Clean Power Association projects that by 2030, the 40,000-plus job openings for electricians will outnumber the qualified professionals available to fill them.
The U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics' job outlook data reveals that wind and solar energy jobs are among the country's top 20 fastest-growing career areas. For the period between 2023 and 2033, employment of solar photovoltaic installers is projected to increase by 48%, and the number of wind turbine technician jobs is expected to increase by a whopping 60%. Both roles involve specialized electrical work, plus other duties depending on the position.
To put these numbers in perspective, the projected employment change for all occupations is 4%, and 11% for electricians for the same period. America, along with much of the rest of the world, is working toward transitioning more and more energy production to renewable sources. This push has created and will continue to generate huge demand for both solar and wind energy careers. If you're interested in joining the field of environmental technology, starting your training as soon as possible can help you capitalize on the demand sooner.
Many electricians will work on solar and wind power equipment, along with other types of electrical work in various settings. This is generally the best option for those who prefer to keep the focus on the electrical work itself. For those who want to do electrical work specific to solar panels, plus other duties related to this form of energy production, training at a solar energy school is worth looking into. Similarly, suppose your interest in wind energy technology goes beyond the related electrical work. In that case, a wind turbine technician training program at a trade school could offer the most direct path to the right career fit for you.


FAQs on Electrician Training and Careers
How Long Does It Take to Become an Electrician?
You can train as an electrician in as little as seven months through a trade school program. However, it usually takes between five and six years to become a journeyman electrician. That's because after completing a vocational program, your actual apprenticeship may last about four or five years. You may sometimes have to wait a few weeks or months for an apprenticeship opportunity to become available since spots are sometimes limited in some regions. However, you may be able to shorten your apprenticeship by getting credit for some of the classroom hours from your pre-apprenticeship program.
What Education Do You Need to Become an Electrician?
At a very minimum, you need a high school (or equivalent) education. But if you genuinely want to succeed, you'll benefit from focusing extra on specific subjects such as math and science during your high school studies. And you may want to pursue at least a small amount of post-secondary education to give yourself the sturdiest foundation you can.
That's because, when it comes to becoming an electrician, education requirements don't vary that much. Regardless of your particular path, you'll need to study and understand subjects such as:
- Reading
- Simple mathematical arithmetic using fractions, whole numbers, decimals, and integers
- Basic algebra
- Geometry, including ratios and proportions
- Units and measurements
- Basic trigonometry
- The physics of electricity
- Electrical power distribution
- Blueprint reading
- Electrical safety
- The National Electric Code
- Electrical components like conduit, panels, switchboards, motors, controllers, generators, and transformers
- Grounding systems and overcurrent devices
- Tools, materials, and job site management
- Testing and problem solving
During your vocational training and apprenticeship, the classroom curriculum at your trade school for electrician training may vary slightly from what you would study at a different school. However, most schools will emphasize some combination of the subjects above.
How Do You Get an Electrician's License?
 It depends on your location and where you plan to work. Licensing requirements vary from state to state and from municipality to municipality. Some states have multiple levels of electrician licensing, whereas others have no licensure requirements. In addition, those states that do require licensure tend to have multiple pathways for attaining it.
It depends on your location and where you plan to work. Licensing requirements vary from state to state and from municipality to municipality. Some states have multiple levels of electrician licensing, whereas others have no licensure requirements. In addition, those states that do require licensure tend to have multiple pathways for attaining it.
That said, the most common way to get electrician licensure is to complete a specified number of hours of classroom instruction and supervised real-world training and then pass an exam. For example, according to California's Department of Industrial Relations, this is how to become an electrician in California if you don't have any prior experience:
- Register as an electrician apprentice or trainee
- Complete at least 720 hours of relevant classroom instruction through a state-approved school (can be part of an apprenticeship)
- Acquire at least 8,000 hours of supervised on-the-job experience from a certified electrician (can be part of an apprenticeship)
- Pass the state certification exam
In New Jersey, the process is similar. However, you do not need to pass an exam to earn certification to practice as a journeyperson electrician. A licensing exam is only required if you want to own an electrical contracting business. So here's what the state's Division of Consumer Affairs says you need to become an electrician in NJ:
- Complete at least 576 hours of classroom instruction
- Accumulate at least 8,000 hours of practical on-the-job experience that involves installing, repairing, or altering electrical wiring
Texas provides another example of how the licensing requirements differ from state to state. There, a license is required for anybody who carries out electrical work. You must also register as an apprentice before training on an actual job site. But the state breaks the trade into multiple levels, each with different requirements. For instance, the state's Department of Licensing and Regulation says that this is how to become an electrician in Texas (at some of the most common levels):
- Residential wireman: Complete 4,000 hours of supervised on-the-job training under the guidance of a licensed residential wireman or master electrician and pass an exam
- Journeyman electrician: Acquire 8,000 hours of supervised on-the-job experience under the direction of a master electrician and pass the required exam
- Master electrician: Accumulate 12,000 hours of supervised on-the-job training as directed by an already-licensed master electrician, maintain a journeyman license for a minimum of two years, and pass the appropriate exam
Again, not all states require licensure. But it is essential to contact your state and the towns and cities you want to work in to determine your requirements. Discover how to become a certified electrician in your region by accessing the tool on The National Occupational Licensing Database website.


How Hard Is It to Become an Electrician?
 Like any other career pursuit, becoming part of the electrical trade can sometimes feel a little challenging. But it can also be a lot of fun. After all, electrician training involves using your hands as well as your mind. In this skilled trade, it's almost impossible to feel bored—especially when you're still learning something new every day.
Like any other career pursuit, becoming part of the electrical trade can sometimes feel a little challenging. But it can also be a lot of fun. After all, electrician training involves using your hands as well as your mind. In this skilled trade, it's almost impossible to feel bored—especially when you're still learning something new every day.
Plus, you'll probably have a lot of support throughout your training. And you'll begin slowly developing your skills and understanding of the trade over time. So, becoming an electrician may not be nearly as challenging as you may think.
However, not everyone puts in the necessary work or stays consistently committed. As a result, they may not be able to earn their license on the first try. So you'll need to study and practice regularly to move ahead and attain your goal of becoming a licensed journeyperson electrician. But if you commit to the journey and stay focused, then you may just exceed your own expectations.
How Much Does It Cost to Become an Electrician?
The cost of becoming an electrician varies enormously. According to the U.S. Department of Education, in the 2021-22 school year, the cost of pre-apprenticeship training at a trade school ranged from $1,246 to $44,820 or more. There are many ways to bring those costs down with scholarships, grants, and other types of financial aid.
Apprenticeship fees can be charged per year. However, many apprentices have their tuition paid by their employer, so you may not be out of pocket for these expenses. Plus, you earn a wage while you complete your training.
What Is a Typical Electrician Salary?
People in the electrical trade often earn good incomes to ensure that our homes, schools, businesses, and industrial buildings stay safely powered. Electrician earnings, however, usually come in the form of hourly wages as opposed to yearly salaries. In 2023, according to the Bureau of Labor Statistics, the median hourly wage of electricians in the U.S. was $29.91, which means electricians make about $61,590 a year for full-time work. Some electricians eventually earn pay as high as $50.09 or more per hour. Of course, pay often varies significantly from region to region.
Also, keep in mind that as an electrician apprentice, you make about half of a fully qualified electrician's wage to start. As you acquire more skills and expertise, you gradually earn pay raises.
Become an Electrician
Many trade schools and technical colleges offer convenient programs that make it easy to learn how to become an electrician and get the skills you need to work in this worthwhile trade.
* While we acknowledge that the term "journeyperson" correctly refers to any gender of tradesperson, we have chosen to also include the more commonly used term "journeyman" and use the terms interchangeably.



